![]()
The following resources offer guidance on how to ensure your social media content is as accessible and inclusive as possible.
Start with general platform-agnostic considerations:
Additional platform-specific guidance is listed below:
General Considerations for Social Media Accessibility
Similar to general web accessibility considerations, follow best practices as much as possible to ensure your social media content is accessible and inclusive. We have compiled a brief list of usability and accessibility tips/strategies below:
- From an accessibility perspective, poor color contrast impacts the readability of your content, especially for individuals with low vision. From a marketing perspective, contrast helps your content stand out to end users. Resources are provided below:
-
- Additional Information:
-
- Tools to help with testing color contrast:
- Colour Contrast Analyser opens a new window (Paciello Group)
- Colorblinding opens a new window (Chrome Extension)
- Tools to help with testing color contrast:
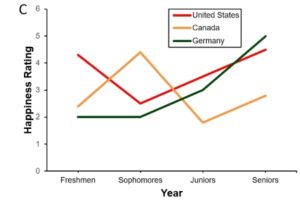
Using color alone to identify or emphasize important information could impact individuals with visual challenges (i.e., low vision, colorblindness).
Example of poor use of color
In this example, the US, Canada, and Germany are identified by color alone.
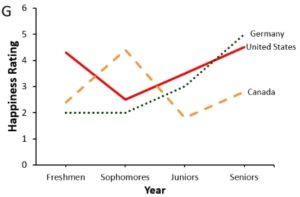
More accessible version of same chart
Using the same chart, now color, line type (i.e., dashed, solid), and labels are used to distinguish between the different countries.
Screen readers will actually read emojis out loud for individuals who are unable to see them (e.g., smiling face, angry face, smiling face with glasses, etc.). Using multiple emojis in one message or placing the most important information after a series of emojis may result in screen reader users bypassing the message altogether.
Resources are provided below:
- How Do People with Visual Impairments Use Emojis? opens a new window (Veronica with Four Eyes Blog)
Social media platforms like Facebook and LinkedIn actually offer you the ability to upload video along with a separate captions file (i.e., .SRT file). Other platforms (e.g., Twitter, Instagram, etc.) will allow you to share video, but you will need to burn the captions into the video before uploading it (i.e., open captions).
Additional Resources:
- Creating Accessible Multimedia Content
- VEED.io opens a new window (can generate auto-subtitles)
- VEED.io offers a quick and easy way to produce burned-in captions for short video clips. The free account allows you to creating burned-in captions for clips less than 10-minutes, but videos are watermarked with VEED.io. An upgraded account allows for removal of the watermark and the ability to work with longer video content. You can then upload the video clips directly to any social media platform.
For short clips it may be possible to place the transcript in the post. For longer recordings, provide a link to a copy of the transcript.
Additional resources:
- Otter.ai opens a new window
- The basic account is free and offers up to 300 free minutes of transcription per month. The transcription also attempts to break down the audio by speaker. Transcribe your audio, host it on your website or web server, and share the link along with the audio recording on your social media account.
- Transcribe using Voice Typing in Google Docs opens a new window
- For short clips, this is another option for creating a quick transcript.
- Open up Google Docs.
- Go to Tools>Voice Typing.
- Select the appropriate speaker language (e.g., English/US) and the start speaking. (NOTE: You also play the audio from your recording, loud enough for the microphone to pick up the speech and transcribe it.)
- For short clips, this is another option for creating a quick transcript.
Audio description or descriptive video is basically a narrator describing what is happening visually in a movie or video clip to individuals with visual impairments. This is typically needed when it is difficult to understand what is happening from the audio alone.
Additional information:
- Guidance coming soon…
Screen reading applications read each character when it encounters a URL. Whenever possible, use services like TinyURL opens a new window and Bitly opens a new window to shorten URLs used in your social media posts.
Additional Resources for Social Media Accessibility
The following resources offer additional general guidance and how-to information for assistive technology users:
- Navigating Social Media with Assistive Technology
- Additional General Guidance for Creating Accessible Social Media
-
- How to add alt text on Social Media opens a new window (Veronica with Four Eyes Blog)
- 5 Steps to Make Accessible and Inclusive Instagram Posts opens a new window (accessiBe Blog)
Still have questions?
If you have additional questions related to making social media accessible, please contact the ATI.
