To create an accessible video review the resources below. Alternatively, videos can be submitted to ATI for captioning and transcripts by submitting a Request Services Form.
To learn more about creating accessible multimedia content, please review the following:
What is Accessible Multimedia?
Making multimedia content accessible benefits all learners (e.g., video streaming in noisy airport). Nonetheless, it is especially beneficial for individuals with hearing loss, those who speak English as a second language, and/or those with learning/cognitive challenges. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) outlines a number of different success criteria for meeting WCAG 1.2 (Provide alternatives for time-based media) opens a new window.
Accessible audio and/or video content should have the following (see Accessible Media for examples):
-
- Transcripts
- Transcripts are required for audio-only content like podcasts. For videos, it is strongly encourage that you post a copy of the transcript along with the video, but it is not required.
- Transcripts
-
- Synchronized, accurate captions
- Synchronized, accurate captions are required for videos (with audio) where it is important that the viewer also follow what is being shown visually.
- Synchronized, accurate captions
-
-
- Possible Exception(s): When the visual content is not important, it is possible to facilitate access simply by providing a copy of the transcript. Here’s an example on YouTube: Interim President Anne Holton discusses Mason’s response to the coronavirus opens a new window
-
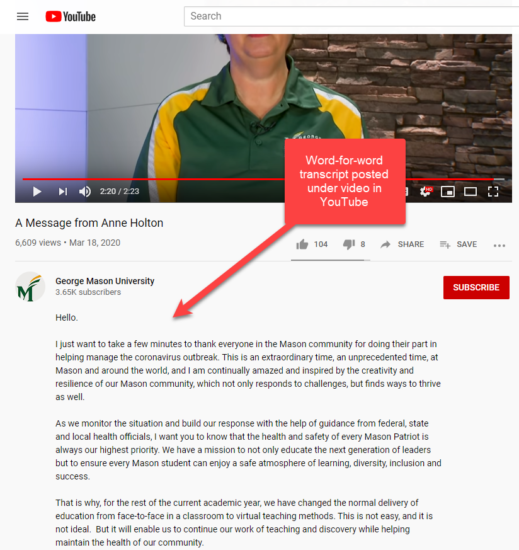
NOTE: Although the video does not have synchronized captions, the text transcript matches the dialog word-for-word. Furthermore, the inability to see the visual imagery would not impact the end-user’s understanding of the content (For more information, see Examples of Success Criteria for Captioning Prerecorded Video opens a new window)
-
- Audio descriptions
- Audio descriptions are required when the visual imagery is important to understanding the content presented in the video
- Audio descriptions
-
- Accessible Video Platform (See Accessible Video Platforms below)
Choosing Accessible Video Players
Creating accessible multimedia is more than just captions, transcripts, and audio description, it is imperative that the player used to deliver the multimedia content be accessible as well. Accessible video players show support the following:
-
- Video buttons and controls should be accessible without use of a mouse
- Video controls should be announced properly to a blind person using screen reading software (e.g., JAWS, NVDA)
- Support for closed captions
- Support for audio description (nice-to-have, but not required)
- Interactive text transcript (nice-to-have, but not required)
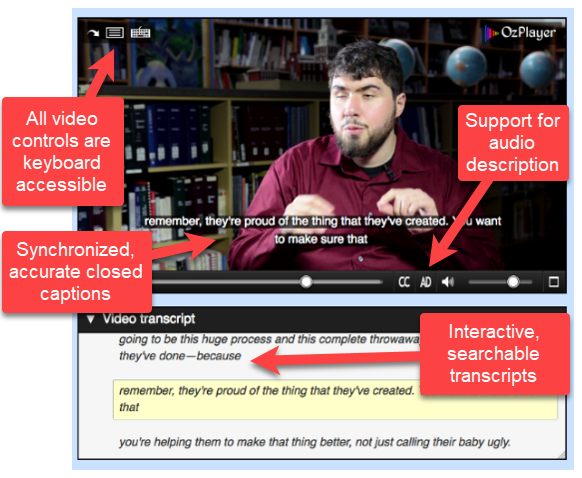
Examples of Accessible Video Players
-
- Fully Accessible Video Players
- OzPlayer (AccessibilityOz), See OzPlayer opens a new window for more information.
- AblePlayer, See AblePlayer opens a new window for more information.
- Fully Accessible Video Players
-
- Keyboard accessible with support for captions (Neither supports audio description unless it is burned directly into the video)
- YouTube (also supports text transcripts)
- Vimeo
- Kaltura
- Keyboard accessible with support for captions (Neither supports audio description unless it is burned directly into the video)
University-Supported Solutions
Lecture capture tools allow instructors to digitally record lectures. The lectures may include audio, videos, PowerPoint slides, and screen capture into a single video for instructors to make available online for students. The following resources cover lecture capture features for solutions supported by Mason:
Kaltura Capture Desktop Recorder
-
- Setting up and installing the Kaltura Capture Desktop Recorder opens a new window tool
- ITS has compiled a great deal of information on the university’s Kaltura implementation. View the Kaltura Knowledge Base on the ITS website for details.
Third-Party Lecture Capture Solutions
PLEASE NOTE: While some 3rd-party solutions may be in use in specific academic departments, they are likely not broadly supported by the university. Please contact the ATI for questions on how to ensure content produced using these tools can be made accessible.
DIY Resources
Below are resources for creating captions and transcripts.
Still have questions?
If you have additional questions related to making media accessible, please contact the ATI.
